60 Minutes Showcases
"Smart" Guns Technology
Friday, November 6, 2015
You may be wondering why CBS 60 Minutes aired a segment on “smart”
guns last Sunday. After all, a gun that will never work in the hands of an
unauthorized person, but that will always work in the hands of everyone else
hasn’t been invented. Even the segment’s reporter, Lesley Stahl, conceded that
there are concerns about whether “smart” guns “work in snow and rain? Will they
work if you`re sweating because an intruder entered your home? Could guns using
wireless technology be hacked or jammed and disabled remotely by the
government?”
There are other, similar concerns too. Would such technology work if, in a defensive situation, a gun were handed off to a family member or other ally? Or if the owner of the gun were wearing a glove? Or, for example, if a right-handed owner were injured and had to hold the gun in his or her left hand? Or whether the electronics would fail if the gun were dropped onto a hard surface. And the list goes on.
Nevertheless, Stahl says, “technology is seeping into every corner of our lives,” and she asks, “Why not guns?”Clearly, part of the answer to her question is that gun owners know that reliable “smart” gun technology has yet to be developed. Just as importantly, though, many gun owners know why gun control supporters are pushing “smart” guns.
For years, gun control supporters frustrated over their failure to convince Congress and state legislatures to ban handguns have been looking for indirect ways to accomplish their goal. A generation ago, they advocated that the Consumer Products Safety Commission be empowered to decide which firearms were safe enough to be permitted for sale, based upon the assumption that the commission would conclude that no handguns met that standard.
In 1994, the Violence Policy Center, formed and led by handgun prohibition advocate Josh Sugarmann, alternately advocated empowering the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives “to operate as a health and safety agency with the ability to set safety standards for firearms [and] restrict the availability of specific firearms, classes of firearms and firearm products [when] the products present an unreasonable risk of death or injury and no feasible safety standard would adequately reduce the risk.” Under such a regimen, the group said, “Handguns should be banned from future sale except for military and law-enforcement personnel.”
In 2000, Hillary Clinton signed on to the Democratic Leadership Council’s New Agenda for the New Decade, which called for policies to “Develop and require ‘smart gun’ technology to prevent use of firearms by unauthorized persons and implement sensible gun control measures.” (Emphasis added.) Mrs. Clinton is, of course, now running for president and has declared that gun control will be one of her priorities. Everytown for Gun Safety is on-board with the push for a “smart” gun requirement too, saying, “Smart guns are going to save lives . . . . [W]hy wouldn’t we want to make guns as safe a consumer product as possible?”
CBS recognizes that Congress and the states won’t limit the manufacture and sale of guns to those that possess “smart” technology unless the voters—many of whom are gun owners—want them to do so. With that in mind, Stahl asked, “Why not let the market decide?”
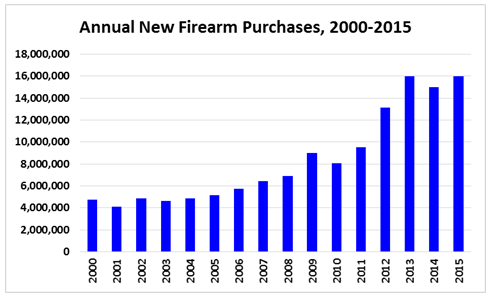
By one measure, at least, the market has decided. According to federal data, since 2000, when Mrs. Clinton endorsed a “smart” gun mandate, Americans have bought approximately 150 million newly-manufactured firearms of conventional type, and annual purchases of conventional firearms have more than tripled. (Estimate for 2015 based upon figures for the first 10 months of the year.)
There are other, similar concerns too. Would such technology work if, in a defensive situation, a gun were handed off to a family member or other ally? Or if the owner of the gun were wearing a glove? Or, for example, if a right-handed owner were injured and had to hold the gun in his or her left hand? Or whether the electronics would fail if the gun were dropped onto a hard surface. And the list goes on.
Nevertheless, Stahl says, “technology is seeping into every corner of our lives,” and she asks, “Why not guns?”Clearly, part of the answer to her question is that gun owners know that reliable “smart” gun technology has yet to be developed. Just as importantly, though, many gun owners know why gun control supporters are pushing “smart” guns.
For years, gun control supporters frustrated over their failure to convince Congress and state legislatures to ban handguns have been looking for indirect ways to accomplish their goal. A generation ago, they advocated that the Consumer Products Safety Commission be empowered to decide which firearms were safe enough to be permitted for sale, based upon the assumption that the commission would conclude that no handguns met that standard.
In 1994, the Violence Policy Center, formed and led by handgun prohibition advocate Josh Sugarmann, alternately advocated empowering the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives “to operate as a health and safety agency with the ability to set safety standards for firearms [and] restrict the availability of specific firearms, classes of firearms and firearm products [when] the products present an unreasonable risk of death or injury and no feasible safety standard would adequately reduce the risk.” Under such a regimen, the group said, “Handguns should be banned from future sale except for military and law-enforcement personnel.”
In 2000, Hillary Clinton signed on to the Democratic Leadership Council’s New Agenda for the New Decade, which called for policies to “Develop and require ‘smart gun’ technology to prevent use of firearms by unauthorized persons and implement sensible gun control measures.” (Emphasis added.) Mrs. Clinton is, of course, now running for president and has declared that gun control will be one of her priorities. Everytown for Gun Safety is on-board with the push for a “smart” gun requirement too, saying, “Smart guns are going to save lives . . . . [W]hy wouldn’t we want to make guns as safe a consumer product as possible?”
CBS recognizes that Congress and the states won’t limit the manufacture and sale of guns to those that possess “smart” technology unless the voters—many of whom are gun owners—want them to do so. With that in mind, Stahl asked, “Why not let the market decide?”
By one measure, at least, the market has decided. According to federal data, since 2000, when Mrs. Clinton endorsed a “smart” gun mandate, Americans have bought approximately 150 million newly-manufactured firearms of conventional type, and annual purchases of conventional firearms have more than tripled. (Estimate for 2015 based upon figures for the first 10 months of the year.)
While Stahl suggested that “smart” guns are not available
for sale because they’re opposed by the NRA, the NRA doesn’t oppose “smart” gun
technology per se. Rather, it has always opposed prohibiting the sale and
possession of firearms that don’t possess the technology.
Ironically, some of the strongest objections to “smart” guns have been raised by the anti-gun Violence Policy Center. It contends that “[m]aking smart guns available could increase the chances of selling guns to Americans who currently do not own them.” The group further contends that “such technology would have no effect on “straw purchases” of guns,” which it describes as “the most common method used to obtain guns illegally” and which, we would add, is one of the reasons that background checks don’t stop criminals from obtaining guns.
Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms
and Explosives
Stephen McHale
was the chief counsel for the Bureau of
Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, and a deputy administrator for
the Transportation Security
Administration.
Note: Transportation
Security Administration is a division of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Clark Kent Ervin
was the inspector general for the U.S.
Department of Homeland Security, a member of the Homeland Security Advisory Council, and is an analyst for CNN.
Annise
Parker is a member of the Homeland
Security Advisory Council, and an advisory board member for Everytown for Gun Safety.
Everytown
for Gun Safety is a “Gun Safety”
group for guns.
Mayors
Against Illegal Guns is a “Gun
Safety” group for guns.
Americans
for Responsible Solutions is a “Gun
Safety” PAC for guns.
Michael R.
Bloomberg is the founder of Everytown
for Gun Safety, a co-chair for Mayors
Against Illegal Guns, Emma Bloomberg’s
father, was a contributor for the Americans
for Responsible Solutions, a benefactor for the Harlem Children's Zone, and a donor for the Robin Hood Foundation.
George
Soros was a benefactor for the Harlem
Children's Zone, and the chairman for the Foundation to Promote Open Society.
Foundation
to Promote Open Society was a funder for the Harlem Children's Zone, the Robin
Hood Foundation, the International
Rescue Committee, and the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (think
tank).
Emma
Bloomberg was the chief of staff for the Robin Hood Foundation, and Michael
R. Bloomberg’s daughter.
Diane
Sawyer was a director at the Robin
Hood Foundation, and a co-anchor for 60
Minutes.
Scott
Pelley is a correspondent for 60
Minutes, and an overseer at the International
Rescue Committee.
Brian Williams
is a director at the Robin Hood
Foundation, and was an anchor for the NBC
Nightly News.
Tom
Brokaw was a director at the Robin
Hood Foundation, an anchor for the NBC
Nightly News, and is an overseer at the International Rescue Committee.
Jeff
Zucker is a director at the Robin
Hood Foundation, the president of CNN
Worldwide, and was an executive producer for the NBC Nightly News.
CNN Worldwide is
a division of CNN.
Ted
Turner is the founder of CNN,
and a co-chairman for the Nuclear Threat
Initiative (think tank).
Jessica Tuchman Mathews is a director at the Nuclear Threat Initiative (think tank),
was the president of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (think
tank), a director at the American Friends of Bilderberg (think
tank), and a 2008 Bilderberg conference participant (think tank).
Ed Griffin’s interview with
Norman Dodd in 1982
(The investigation into the
Carnegie Endowment for International Peace uncovered the plans for population
control by involving the United
States in war)
Carnegie
Endowment for International Peace (think
tank) was a funder for the Nuclear
Threat Initiative (think tank).
Warren E. Buffett
is an adviser for the Nuclear Threat
Initiative (think tank), and an advisory board member for Everytown for Gun Safety.
Everytown
for Gun Safety is a “Gun Safety”
group for guns.
Annise
Parker is an advisory board member for Everytown
for Gun Safety, and a member of the Homeland
Security Advisory Council.
Clark Kent Ervin
was a member of the Homeland Security
Advisory Council, the inspector general for the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, and is an analyst for CNN.
Transportation
Security Administration is a division of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
Stephen McHale
was a deputy administrator for the Transportation
Security Administration, and the chief counsel for the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.




No comments:
Post a Comment